One of world's largest glacier floods triggered in Greenland
12.12.2024 11:03:34 CET | Københavns Universitet | Pressemeddelelse
For the first time, scientists have observed the release of a massive glacial lake outburst in East Greenland, where more than 3,000 billion liters of meltwater were unleashed in just weeks. This rare, natural flooding event, witnessed by University of Copenhagen researchers, provides new insight into the immense and potentially hazardous forces that meltwater can unleash.
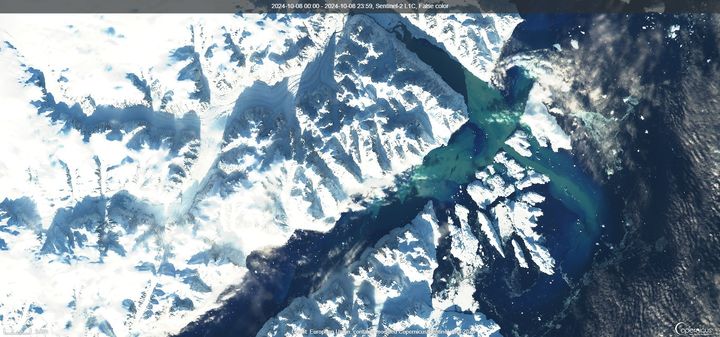
Imagine an enormous bathtub atop a mountain filled with water equivalent to three times Denmark’s annual water consumption, and then suddenly bursting. This is essentially what happened when the massive Catalina Lake in East Greenland released 3.4 cubic kilometers of meltwater – 3,000 billion liters – into the Scoresby Sound fjord.
The enormous volume places this event among the top three largest of its kind ever documented. The meltwater outburst flood occurred between September 23 and October 11, during which the lake’s water level plummeted 154 meters. The dramatic phenomenon was observed for the first time in real time using satellite imagery by scientists from the University of Copenhagen’s Niels Bohr Institute.
"We have previously found traces of similar outburst floods, but due to polar night and clouds obstructing the potential for satellite observations, this is the first time that researchers have been able to monitor an event and measure the water volumes in real time," explains Niels Bohr Institute climate researcher Aslak Grinsted.
View video and animations on our website
Threatens millions of people
The outburst flood in East Greenland occurred because meltwater from Catalina Lake had been accumulating over the past twenty years. The lake is situated in a valley blocked by the massive Edward Bailey Glacier. As the lake filled, the water began to lift the glacier, carving a 25-kilometer-long tunnel beneath the ice, through which the water eventually burst into the world’s largest fjord, Scoresby Sound.
This phenomenon, where a glacial lake gradually fills and then releases its water in a sudden flood, is known as a Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF). Such events have become increasingly frequent over the last three decades due to rising global temperatures and climate change.
“The danger from glacier-dammed lakes is increasing due to global warming. It’s vital to improve our understanding of this phenomenon to issue timely warnings should there be an imminent risk,” says Grinsted.
While glacial lake outburst floods can be catastrophic in densely populated areas like the Himalayas, where they often destroy villages, this particular outburst caused no harm due to Greenland’s sparse population. However, a 2023 study concluded that 15 million people worldwide live under the threat of deadly glacial floods.
“I expect that we will witness outbursts from even larger ice-dammed lakes as Greenland’s ice sheet retreats in coming centuries. At the end of the last Ice Age, Lake Missoula had an outburst that was 2,500 times larger than the recent Catalina event. To understand these massive forces, we must study the largest outbursts when they occur,” says Aslak Grinsted.
Facts:
Comparable to the energy of the world’s largest nuclear power plant
The energy released by glacial lake outburst floods is staggering.
“In this case, the energy released by the glacier flood was equivalent to the output of the world’s largest nuclear power plant running at full capacity for 22 days,” explains Aslak Grinsted.
According to the researcher, it’s worth considering how to harness the immense energy of such natural phenomena as a source of green energy. In theory, the energy released from the Catalina Lake event could have continuously provided 50 megawatts of electricity, enough to meet the needs of a small town. However, in this instance, the nearest settlement is 180 kilometers away and inhabited by a mere 350 residents – posing a significant technological challenge for energy utilization.
“As with many other natural resources in Greenland, infrastructure is a problem. But if a brilliant engineer could figure out how to harness these meltwater outbursts, there’s enormous power and energy potential in them,” concludes Grinsted.
- This Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) ranks among the top three largest measured by volume in global history and top 10 by outflow rate.
- 3.4 cubic kilometers of meltwater were released – equivalent to 3.4 billion tons of water and approximately three times Denmark’s annual water consumption.
- The outburst occurred over roughly 20 days, with a peak discharge rate of 7,200 cubic meters persecond – more than twice the flow of Niagara Falls at peak season (approximately 2,800 cubic meters per second).
- Historically, over 12,000 people worldwide have died due to GLOFs, most in South America and Central Asia.
- Since the 1990s, the number and size of glacial lakes have increased significantly.
Kontakter
Aslak Grinsted
Niels Bohr Institute
Københavns Universitet
aslak@nbi.ku.dk
+4531380716
Michael Skov Jensen
Journalist and Team Coordinator
The Faculty of Science
University of Copenhagen
+45 93 56 58 97
msj@science.ku.dk
Følg pressemeddelelser fra Københavns Universitet
Skriv dig op her, og modtag pressemeddelelser på e-mail. Indtast din e-mail, klik på abonner, og følg instruktionerne i den udsendte e-mail.
Flere pressemeddelelser fra Københavns Universitet
Københavns Universitet lancerer stor vidensportal til kvinder i overgangsalderen5.3.2026 11:00:00 CET | Pressemeddelelse
Mange kvinder mangler viden om overgangsalderen, som længe har været et underprioriteret emne. En pjece og en ny vidensportal fra forskningsinitiativet Kvinder i Sund Overgang (KiSO) ved Københavns Universitet skal hjælpe kvinder med at få overblik og forstå denne fase af livet.
Her er Københavns Universitets valgeksperter4.3.2026 16:14:11 CET | Pressemeddelelse
Folketingsvalget er i gang. Der er stor efterspørgsel på ekspertkilderne. Her er Københavns Universitets liste med et udpluk af forskere, der kan agere eksperter i valgkampen.
Ny rapport: Unge frygter drugging i nattelivet – men anmelder stort set aldrig4.3.2026 06:00:00 CET | Pressemeddelelse
Unge – især kvinder – frygter i stigende grad at blive drugget, og fænomenet er mere omfattende og nuanceret end hidtil antaget. Det viser en ny rapport fra Kriminologisk Observatorium ved Københavns Universitet.
Børn med dårlig tandsundhed har oftere hjerte-kar-sygdomme som voksne2.3.2026 07:00:00 CET | Pressemeddelelse
Huller i tænderne og svær tandkødsbetændelse i barndommen kobles sammen med markant højere forekomst af hjertestop, hjerneblødning og åreforkalkning i voksenlivet, viser nyt studie fra Københavns Universitet.
Heste fløjter og synger, når de vrinsker23.2.2026 05:00:00 CET | Pressemeddelelse
Ny forskning fra Københavns Universitet viser, at et hestevrinsk er mere komplekst end som så. Opdagelsen bryder med tidligere antagelser om det store pattedyr og kaster nyt lys over, hvordan heste kommunikerer. Et forskningsområde, der trods 4.000 års domesticering stadig er fyldt med ubesvarede spørgsmål.
I vores nyhedsrum kan du læse alle vores pressemeddelelser, tilgå materiale i form af billeder og dokumenter samt finde vores kontaktoplysninger.
Besøg vores nyhedsrum