AI successfully helps detecting more breast cancers around Danish capital
AI has helped to detect significantly more cases of breast cancer and reduce radiologist workloads. These are among the main conclusions of a new evaluation study from the University of Copenhagen and Capital Region of Denmark after nearly three years of using artificial intelligence for breast cancer detection in screening mammography.
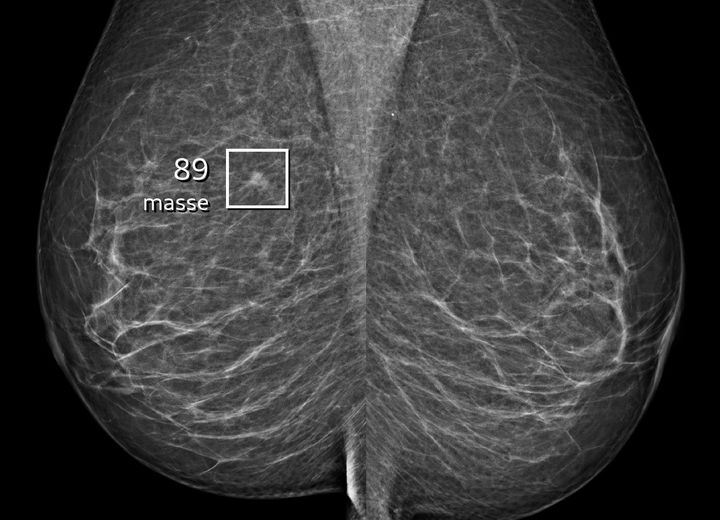
Can artificial intelligence be used to help detect breast cancer? The answer is an unequivocal 'yes' according to a new study from the University of Copenhagen’s Department of Computer Science and the Capital Region of Denmark’s breast cancer screening programme.
The study, an evaluation of the region's deployment of AI over nearly three years, demonstrates that the synergy between expert breast radiologists and the AI system results in significantly more cases of breast cancer being detected and the number of false positive results being reduced.
All Danish women between the ages of 50 and 69 are offered breast cancer screening every two years. Those who have already had breast cancer surgery are offered mammograms until the age of 79. All in all, tens of thousands of X-rays are now being examined by artificial intelligence every year.
"Screening an entire population using mammography results in fewer breast cancer deaths, but also places greater demands on radiologists. In the study, we conclude that artificial intelligence is a great help, and when combined with the assessments of experienced specialists, there are more cases of breast cancer caught in their early stages and fewer false positive results than before AI was introduced," says postdoc Andreas Lauritzen from the Department of Computer Science, the study’s first author.
Prior to the introduction of AI, radiologists detected an average of 70 cases of breast cancer in every 10,000 screenings. Since being implemented, AI has allowed radiologists to find 82 women with breast cancer out of every 10,000, an increase of 12 cases per 10,000 screenings.
More small tumours detected
The researchers compared two groups of 119,000 women between the ages of 50 and 69 who underwent mammography screening in Denmark’s Capital Region. The first group was screened between October 2020 and November 2021 without the use of AI. The second group was screened between November 2021 and October 2022 with the help of AI to analyse the images.
In addition to the fact that more cases of breast cancer were detected by the combination of radiologists and AI, a larger proportion of the cases involved small invasive tumours of one centimetre or less. The proportion of small tumours detected with the help of AI was 44.93 per cent compared to 36.60 per cent prior to the introduction of AI – a major bonus for the treatment of these women.
"Both the number of tumours found and their size are crucial factors that really have an impact on these women's likelihood of being cured," explains Dr. Ilse Vejborg, Chief Physician and Head of the Capital Mammography Screening Programme in Denmark. Dr. Vejborg is responsible for the implementation of AI in the screening programme.
Help for busy radiologists
The use of artificial intelligence in Denmark’s Capital Region has also led to a 33.4 percent reduction in the assessment workload for breast radiologists. Radiologists used to double read many thousands of X-rays while screening the entire population, most of which turned out to be normal.
Prior to the introduction of artificial intelligence, all mammograms were read independently by two breast radiologists. Now, the AI screening system automatically selects approximately 70 percent of the lowest risk mammograms, which are then read by a single experienced breast radiologist.
"There is a shortage of breast radiology specialists in the Capital Region of Denmark and the rest of the country – as well as around the world. At the same time, the share of the population that is older has gotten larger, meaning that more people need to be screened. As such, our goal was to reduce the workload without compromising quality, which we have succeeded in doing," says Dr. Vejborg.
The remaining 30 percent of mammograms go through an independent double reading by two radiologists who can then use the AI system as a tool to automatically hone in on any suspicious lesions on the X-rays. Consequently, all examinations are assessed by at least one experienced breast radiologist, and the final result is always decided by breast radiologists.
For examinations where there is disagreement, the two breast radiologists meet for a consensus discussion or bring in a third experienced breast radiologist to help make a final decision. Therefore, an experienced breast radiologist always determines the ultimate course of action. This applies if there is disagreement between the AI's assessment or disagreement between the two radiologists.
Fact box: More about the AI and study results
- The AI system that was used is trained to identify suspicious areas in mammograms using advanced deep learning models.
- More than 119,000 women were involved in the study.
- AI-assisted screenings detected more cases of breast cancer (0.82% vs. 0.70%) and reduced false positives (1.63% vs. 2.39%).
- AI assistance also helped to reduce the percentage of women called back in for assessment by 20.5 percent and the workload of breast radiologists to assess screening examinations by 33.4 percent.
- Furthermore, the positive predictive value of AI-assisted screening was higher (33.5% vs. 22.5%), and more of the invasive cancers detected were smaller than 1 cm (44.93% vs. 36.60%).
Kontakter
Andreas Lauritzen
Postdoc
Department of Computer Science
University of Copenhagen
+45 22 72 41 99
al@di.ku.dk
Ilse Vejborg
Chief Physician and Head of Capital Mammography Screening Program and
Department of Breast Examinations, Herlev-Gentofte Hospital/ Capital Mammography Screening Programme
Capital Region of Denmark
Ilse.vejborg@regionh.dk
Michael Skov Jensen
Journalist and team coordinator
The Faculty of Science
University of Copenhagen
+ 45 93 56 58 97
msj@science.ku.dk
Følg pressemeddelelser fra Københavns Universitet - Det Natur- og Biovidenskabelige Fakultet
Skriv dig op her, og modtag pressemeddelelser på e-mail. Indtast din e-mail, klik på abonner, og følg instruktionerne i den udsendte e-mail.
Flere pressemeddelelser fra Københavns Universitet - Det Natur- og Biovidenskabelige Fakultet
Old aerial photos give scientists a new tool to predict sea level rise3.7.2025 08:00:00 CEST | Press release
Researchers from the University of Copenhagen have gained unique insight into the mechanisms behind the collapse of Antarctic ice shelves, which are crucial for sea level rise in the Northern Hemisphere. The discovery of old aerial photos has provided an unparalleled dataset that can improve predictions of sea level rise and how we should prioritise coastal protection and other forms of climate adaptation.
Gamle luftfotos giver forskere nyt redskab til at forudsige havstigninger3.7.2025 08:00:00 CEST | Pressemeddelelse
Forskere fra Københavns Universitet har fået unik adgang til at forstå mekanismerne bag antarktiske ishylders kollaps, som er afgørende for havstigninger på den nordlige halvkugle. Et fund af gamle luftfotos har skabt et enestående datasæt, som kan forbedre vores forudsigelser af hvor meget havene stiger, og vores prioritering af kystsikring og andre klimatilpasninger.
Ny institutleder på IFRO: ”Faglighed og fællesskab går hånd i hånd”1.7.2025 10:49:17 CEST | Pressemeddelelse
Per Svejstrup er fra 1. august ansat som institutleder på Institut for Fødevare- og Ressourceøkonomi (IFRO). Den kommende leder træder ind i rollen med stor respekt for IFRO's faglige og kollegiale kultur med klare ambitioner for fremtiden.
Dangerous Variant of Salmonella Still Not Eradicated – Researchers Point to the Solutions1.7.2025 09:53:23 CEST | Press release
The infectious and multi-resistant cattle disease Salmonella Dublin can be fatal to both humans and animals and causes significant losses for farmers. Although Denmark has attempted to eradicate the disease since 2008, it has not yet succeeded. A study from the University of Copenhagen points to possible reasons – and the necessary solutions.
Farlig type salmonella er stadig ikke nedkæmpet i Danmark – forskere peger på løsningerne30.6.2025 09:54:03 CEST | Pressemeddelelse
Den smitsomme og multiresistente kvægsygdom Salmonella Dublin kan være dødelig for både mennesker og dyr og medfører desuden betydelige tab for landmændene. Selvom Danmark har forsøgt at udrydde sygdommen siden 2008, er det ikke lykkedes. Et studie fra Københavns Universitet peger på den mulige årsag og de nødvendige løsninger.
I vores nyhedsrum kan du læse alle vores pressemeddelelser, tilgå materiale i form af billeder og dokumenter samt finde vores kontaktoplysninger.
Besøg vores nyhedsrum