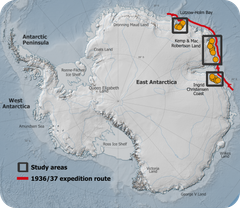
Local bright spot among melting glaciers: 2000 km of Antarctic ice-covered coastline has been stable for 85 years
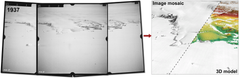
A whaler's forgotten aerial photos from 1937 have given researchers at the University of Copenhagen the most detailed picture of the ice evolution in East Antarctica to date. The results show that the ice has remained stable and even grown slightly over almost a century, though scientists observe early signs of weakening. The research offers new insights that enhance predictions of ice changes and sea level rise.
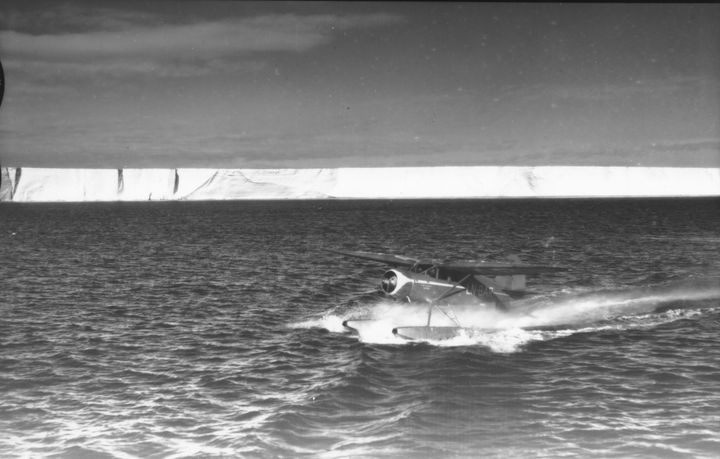

Higher temperatures, extreme weather, melting glaciers, and rising sea levels - all indicators that the climate and the world's ice masses are in a critical state. However, a new study from the Department of Geosciences and Natural Resource Management at the University of Copenhagen offers a local bright spot.
Using hundreds of old aerial photographs dating back to 1937, combined with modern computer technology, the researchers have tracked the evolution of glaciers in East Antarctica. The area covers approximately 2000 kilometers of coastline and contains as much ice as the entire Greenland Ice Sheet.
By comparing the historical aerial photos with modern satellite data, the researchers have been able to determine whether the glaciers have retreated or advanced and whether they have thickened or thinned. The study reveals that the ice has not only remained stable but grown slightly over the last 85 years, partly due to increasing snowfall.
“We constantly hear about climate change and new melt records, so it's refreshing to observe an area of glaciers that has remained stable for almost a century,” says PhD student Mads Dømgaard, the study’s first author.
However, the researcher emphasizes that the study also shows the first signs of changes in the sea ice off the glacier. This could mean that the stable East Antarctic glaciers might shrink in the future.
“Our results also indicate weakening sea ice conditions, making the glaciers’ floating ice tongues more vulnerable and unable to grow as large as seen in the early aerial images from 1937. We know from other parts of Antarctica that the ocean plays an extremely important role and drives the massive and increasing melt we see in e.g. West Antarctica,” says Mads Dømgaard.
Hidden from the Nazis
Most of the images used in the study were captured during a 1937 expedition organized and paid for by Norwegian whaler Lars Christensen. The mission aimed to produce the first maps of this part of East Antarctica, but the maps were never published due to the German invasion of Norway. Since then, the images have been stored at the Norwegian Polar Institute in Tromsø and forgotten.
When the researchers from the University of Copenhagen read about the expedition, they realized that valuable images were likely hidden in an archive in Norway. They traveled to Tromsø and reviewed all 2200 images taken during the expedition. They supplemented the Norwegian aerial images with images of the same glaciers from Australian surveys conducted between 1950 and 1974.
“By comparing the historical aerial photos with modern satellite data, we have gained critical knowledge about glaciers that we would not otherwise have had. I think it's fantastic that these old images can be used to generated new research results almost 100 years after they were taken,” says Assistant Professor Anders Bjørk from the University of Copenhagen, who leads the group working with the historical images.
Potential for major sea level rise
The Antarctic Ice Sheet is receiving increasing attention from researchers, due to its potential for extremely large and rapid sea level rise. Unlike Greenland, very little was known about Antarctica glaciers until the 1990s, when the first good satellite observations became available.
“Early observations of glaciers are extremely valuable as they give us a unique insight into how the ice has evolved through a varying climate and whether current changes in the ice exceed the glaciers' normal cycle of advance and retreat,” explains Mads Dømgaard.
According to the researcher, solid, long-term data is crucial for producing accurate predictions of future glacier evolutions and sea level rise, and this study provides new insights into a vast area in East Antarctica.
“The long time series of glaciers improves our ability to make more accurate models of future ice changes, as the models are trained on historical observations,” concludes Anders Bjørk.
The results have just been published in Nature Communications [link ] and are a collaboration between researchers from the University of Copenhagen, the Norwegian Polar Institute, the Arctic University of Norway and the Institute of Environmental Geosciences in France.
More about the study
- Out of 2200 images photographed from seaplanes in 1937, 130 were selected for the analysis.
- The researchers combined the historical photos with modern satellite data to create 3D reconstructions of the glaciers.
- The Norwegian aerial images were supplemented with 165 aerial images of the same glaciers from Australian surveys conducted between 1950 and 1974. This allowed the researchers to examine the evolution of the glaciers over different periods and calculate historical ice flow speeds for selected glaciers.
- Compared to modern data, the ice flow speeds are unchanged. While some glaciers have thinned over shorter intermediate periods of 10-20 years, they have remained stable or grown slightly in the long term, indicating a system in balance.
- The research is funded by the Villum Foundation.
Kontakter
Mads Dømgaard
PhD student
Department of Geosciences and Natural Resource Management
University of Copenhagen
+45 60 83 53 05
mld@ign.ku.dk
Anders Bjørk
Assistant Professor
Department of Geosciences and Natural Resource Management
University of Copenhagen
+ 45 29 92 17 42
aab@ign.ku.dk
Michael Skov Jensen
Journalist and team coordinator
Faculty of Science
University of Copenhagen
+45 93 56 58 97
msj@science.ku.dk
Billeder


Følg pressemeddelelser fra Københavns Universitet
Skriv dig op her, og modtag pressemeddelelser på e-mail. Indtast din e-mail, klik på abonner, og følg instruktionerne i den udsendte e-mail.
Flere pressemeddelelser fra Københavns Universitet
Fermentering gør havets grøntsager mere spiselige5.12.2025 06:18:59 CET | Pressemeddelelse
Tang har længe været hyldet som en bæredygtig superingrediens – men dens “fiskede” smag er en barriere for mange vestlige forbrugere. Nu viser et nyt studie fra Københavns Universitet, at fermentering med mælkesyrebakterier kan være nøglen til at få tangen til at glide ned.
P-piller kan forringe kvinders mentale trivsel2.12.2025 06:05:00 CET | Pressemeddelelse
Adgang til p-piller i ungdomsårene er forbundet med øget risiko for depression senere i livet. Især kan kvinder, der er genetisk disponeret for psykisk sygdom, risikere at blive ramt af bivirkningen. Det viser et nyt studie fra Københavns Universitet.
Psykologer: Derfor kan protester samle folk på tværs af politiske skel27.11.2025 09:18:05 CET | Pressemeddelelse
Hvordan kan mennesker med diametralt modsatte holdninger pludselig stå skulder ved skulder i protest? Det spørgsmål har et internationalt forskerhold undersøgt. Udgangspunktet er COVID-protesterne, som blev båret af tre samlende strategier.
Sådan bruger planter ingeniørprincipper til at trænge gennem hård jord27.11.2025 07:16:00 CET | Pressemeddelelse
Et internationalt forskerhold med Københavns Universitet, Shanghai Jiao Tong University og University of Nottingham i spidsen har opdaget, hvordan planterødder er i stand til at trænge igennem hård og tæt jord ved hjælp af et velkendt ingeniørprincip. Opdagelsen kan få stor betydning for fremtidens afgrøder i en tid, hvor presset på landbrugsjorden stiger.
Forskere advarer: Klimaforandringer kan udvide levesteder for malariamyg27.11.2025 06:00:00 CET | Pressemeddelelse
Hvis vi ikke begrænser klimaforandringerne, så risikerer vi, at malariamyg udbreder deres levesteder i Afrika betydeligt. Det vil udsætte mange hundrede millioner mennesker for en højere smitterisiko.
I vores nyhedsrum kan du læse alle vores pressemeddelelser, tilgå materiale i form af billeder og dokumenter samt finde vores kontaktoplysninger.
Besøg vores nyhedsrum