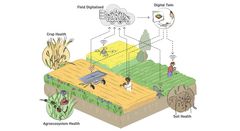
Robots, monitoring and healthy ecosystems could halve pesticide use without hurting productivity
Smarter crop farming that combats weeds, insect pests and plant diseases by integrating modern technologies like AI-based monitoring, robotics, and next-generation biotechnology with healthy and resilient agricultural ecosystems: One Crop Health, a new research collaboration based at University of Copenhagen aims to reduce the use of pesticides by developing a sustainable agriculture for the future.

In keeping with the age-old saying: ‘prevention is better than a cure’ more sustainable approaches should await the farmers of the future without compromising their productivity, as envisioned by the researchers leading the recently launched One Crop Health research project.
Backed by DKK 60 million (€8.05M) from Novo Nordisk, researchers from University of Copenhagen will gather knowledge over the next six years to develop smarter agriculture that is both sustainable and able to produce enough food for the world's growing population in a collaboration with researchers from Aarhus University and Rothamsted Research in the UK.
For many years, growers have relied on pesticides to control disease, pests and weeds, which lead to worldwide losses of one-third of crop yield. At the same time, estimates show that we will need 60% more food than today by 2050.
However, pesticides also threaten health, nature and biodiversity, and there is increasing pressure from society and politicians to limit their use. Recently the desire for healthier and more sustainable crops resulted in EU policy plans for a 50% reduction in pesticides by 2030. These plans have now been set on pause after being challenged by farmers concerned that pesticide reduction could make farming unviable by hurting productivity.
So, can growers halve their use of pesticides without the profession becoming unproductive and the world running out of food or? This is the central question that One Crop Health seeks to answer.
Making pesticide reduction profitable for farmers
“The political controversy, farmer and industry concern, and the uncertainty over regulation clearly shows that more research is needed to enable this transition. Most farmers actually want to use less pesticides, but there is a need for research that demonstrates how this is possible whilst maintaining healthy, high-yielding, and profitable crops. The One Crop Health project aims to bridge the gap by developing research, which places the drive to reduce pesticide use on a scientific foundation that will ultimately help farmers make the rational decision to help reduce pesticide use,” says Professor Paul Neve from the Department of Plant and Environmental Sciences
According to the project's lead researcher, making a viable transition is possible though, using a more holistic approach to farming.
"Generally the focus needs to move away from solving individual problems by way of a few blunt tools like pesticides. Oftentimes, this approach creates new problems elsewhere, which then also need to be addressed. Planting fields densely to avoid weeds is another example of this lack of oversight, where the misguided solution ends up creating the optimal conditions for fungi and diseases instead. We need to get better at understanding entire ecosystems and then make use of all of the modern tools available," says Professor Paul Neve.
"If we can create healthy ecosystems that will reduce the numbers of pests, weed and diseases, it will simply reduce the need for spraying. We can largely replace the remaining need with other tools, for example, AI-based monitoring and modelling can help to inform where and when pests need to be controlled and new solutions such as bio-pesticides can be used to achieve that," he says.
Natural defenses have been replaced with chemicals
The resilience that results from healthy ecosystems can reduce challenges that are currently solved by means like pesticides.
"Today’s crops are characterized by attempts to make crop production more efficient for thousands of years. In the process, many crops have lost their natural defences against pests, weeds and diseases," explains Paul Neve.
According to the researcher, tomorrow’s growers can get better at protecting their plants by looking at how things are done in nature. Here, helpful microorganisms like bacteria and fungi protect against diseases, and healthy crops are more competitive against weeds. At the same time, pests that threaten crops will be better controlled by their natural enemies.
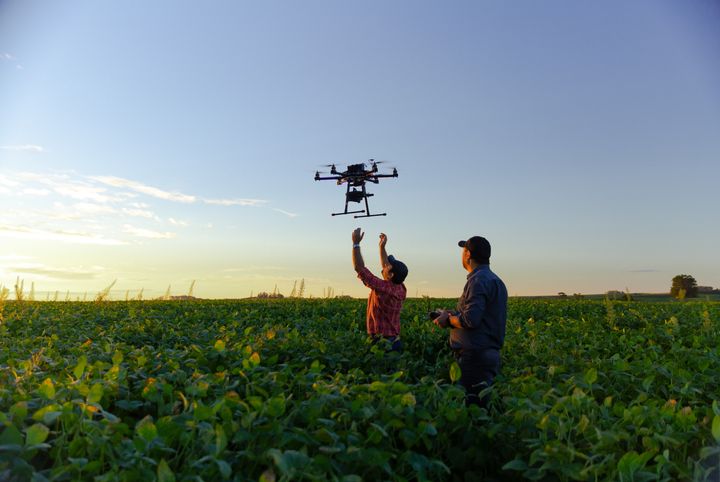
"If you think of the field as an entire ecosystem that needs to thrive – hence the name One Crop Health, we believe you get a preventive overall effect. At the same time, modern knowledge and technology can, for example, change the basic need for pesticides. Whereas entire fields are sprayed today, drone surveillance will allow us to only target where weeds are a threat to the crop, or not at all, and let robots do the work instead," says the professor.
100 farmers to help researchers
“Part of the project is about working with farmers, using their fields to discover smart solutions, so future agriculture can be based on the best possible knowledge," says Paul Neve.
In collaboration with 100 farms, and distributed equally across Denmark and England, they will begin by collecting data from scratch.
"We begin by asking farmers about their current challenges, how they will try to solve them and about what works and what doesn’t. To this knowledge bank, we will add our professional knowledge of ecosystems, modern technologies and methods, and then the goal when the six years have passed is to be able to give a lot of knowledge and concrete methods back to farmers," says Paul Neve.
Drone data and models will predict field needs
The final prong in the effort to achieve a holistic understanding comes from broad knowledge and modern technologies that provide access.
In an interdisciplinary collaboration with the Department of Computer Science at University of Copenhagen, a group of computer scientists will translate information from surveillance with modern technologies such as drones, and on that basis design so-called digital twins of farmer’s fields.
"They will provide a kind of model that can predict how fields will behave, the needs that are just around the corner and how different solutions will affect the fields," says Paul Neve.
In the second half of the six-year project, 11 Ph.D. students will develop knowledge about specific solutions within their respective focus areas.
"When the six years have passed, it is important for us that we have integrated data and new tools in a holistic way, providing farmers with concrete methods that they can use to solve their challenges in everyday life more sustainably without compromising productivity," Paul Neve concludes.
Keywords
Contacts
Paul NeveProfessorSection for Crop Sciences, Department of Plant and Environmental Sciences, University of Copenhagen
Tel:+45 35 32 21 61pbneve@plen.ku.dkKristian Bjørn-HansenJournalist and Press ContactFaculty of Science, Copenhagen University
Tel:+45 93516002kbh@science.ku.dkImages
Links
ABOUT THE FACULTY OF SCIENCE
The Faculty of Science at the University of Copenhagen – or SCIENCE – is Denmark's largest science research and education institution.
The Faculty's most important task is to contribute to solving the major challenges facing the rapidly changing world with increased pressure on, among other things, natural resources and significant climate change, both nationally and globally.
Subscribe to releases from Københavns Universitet - Det Natur- og Biovidenskabelige Fakultet
Subscribe to all the latest releases from Københavns Universitet - Det Natur- og Biovidenskabelige Fakultet by registering your e-mail address below. You can unsubscribe at any time.
Latest releases from Københavns Universitet - Det Natur- og Biovidenskabelige Fakultet
Ox-eye daisy, bellis and yarrow: Flower strips with at least two sown species provide 70 percent more natural enemies of pests22.5.2025 09:26:48 CEST | Press release
Planting flower strips in a field with at least two species can increase the number of natural enemies of pests by 70 percent. The more flower species, the better the effect, according to a new meta-analysis from the University of Copenhagen.
Okseøje, bellis og røllike: Blomsterstriber med mindst to arter giver 70% flere af skadedyrenes naturlige fjender22.5.2025 07:07:00 CEST | Pressemeddelelse
Planter man blomsterstriber på sin mark med mindst to arter, kan det øge antallet af naturlige fjender af skadedyr med over 70%. Jo flere blomsterarter, jo bedre effekt, viser et nyt metastudie fra Københavns Universitet.
Scientific breakthrough: We can now halve the price of costly cancer drug19.5.2025 10:18:56 CEST | Press release
The demand for the widely used cancer drug Taxol is increasing, but it’s difficult and expensive to produce because it hasn’t been possible to do it biosynthetically. Until now, that is. Researchers from the University of Copenhagen have cracked the last part of a code that science has struggled with for 30 years. The breakthrough could halve the price of the drug and make production far more sustainable.
Forskningsgennembrud: Nu kan vi halvere prisen på dyrt kræftmiddel19.5.2025 07:16:00 CEST | Pressemeddelelse
Efterspørgslen på det udbredte kræftmiddel taxol stiger, men stoffet er svært og dyrt at lave, fordi man ikke har kunnet fremstille det biosyntetisk. Ikke før nu. Forskere fra Københavns Universitet har nemlig knækket den sidste del af en kode, som videnskaben har bakset med i 30 år. Gennembruddet kan halvere prisen på lægemidlet og gøre produktionen langt mere bæredygtig.
Saving the Asian Unicorn – If It Still Exists6.5.2025 09:48:24 CEST | Press release
The saola, an antelope-like bovine, is one of the world’s rarest and most endangered mammals. In fact, it hasn’t been observed in over 10 years. Researchers from the University of Copenhagen, in collaboration with Vietnamese scientists and an international team of researchers, have for the first time mapped the saola’s complete genome, and they have used that knowledge to estimate the chances of saving it – if it still exists.
In our pressroom you can read all our latest releases, find our press contacts, images, documents and other relevant information about us.
Visit our pressroom